The condyles form a flat surface known as the tibial plateau. Proximal medial tibia inferior to medial condyle Action.

Femur An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
It works as a static knee stabilizer against valgus rotation of the knee joint.
. The pectineal line is located proximal and medial on the posterior femur. When viewed from the axial plane the shape of the distal femur is trapezoidal. Medial and lateral.
The meaning of CONDYLE is an articular prominence of a bone. Trochanteric anastomosis cruciate anastomosis. Hence it prevents separation of medial tibia and femoral condyles following a blow outside the corresponding knee.
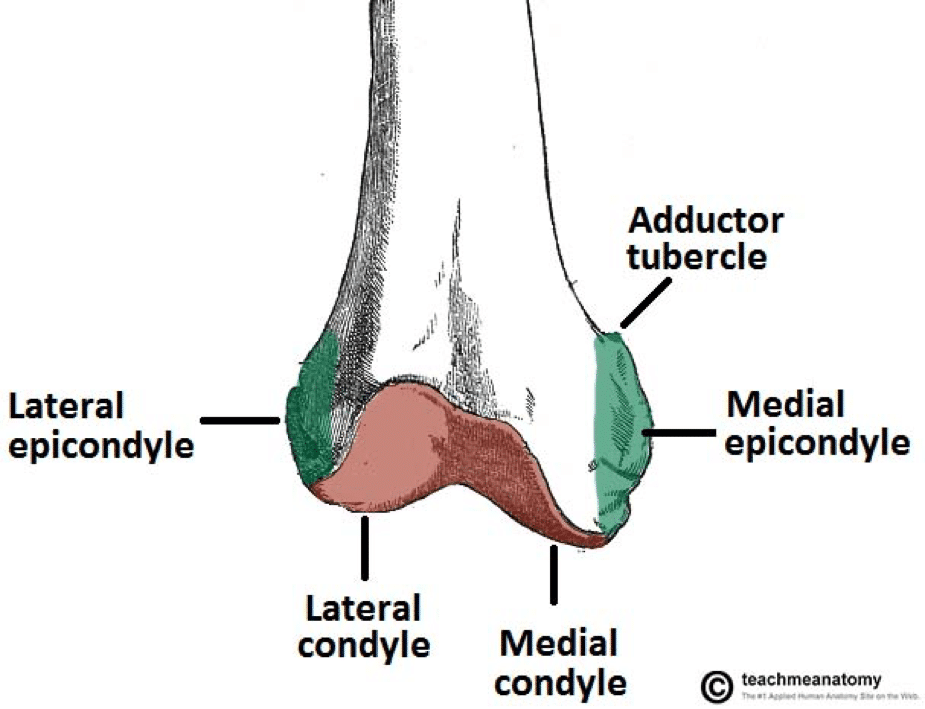
A rough line called the linea asperaruns almost the full length of the posterior femur. Distally on the femur are the lateral and medial condyles which articulate with the tibia below. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral outer condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee.
Gluteal tuberosity of femur iliotibial band of fasciae latae. Fovea of Femur Head Fovea capitis fe-moris is a small pit-like depression on the medial surface of the head which is also called the fovea capitisIt is as an attachment site for the ligamentum teres round ligament. Rounded medial and lateral condyles are located on the distal end of the femur and articulate with the tibia.
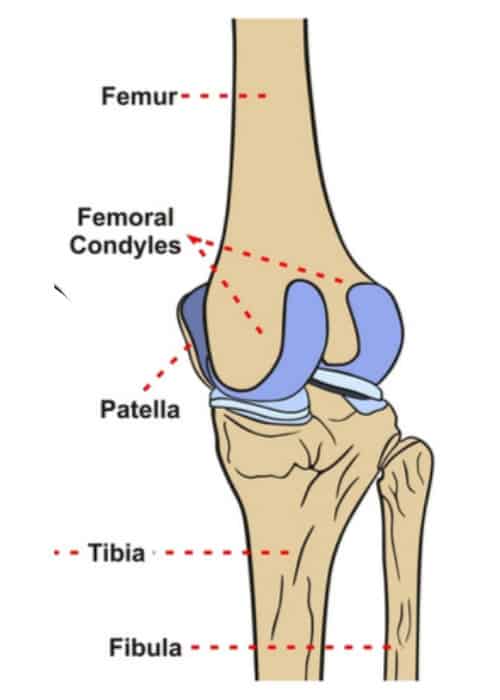
These communicate through open centres of the menisci where the condyles of the femur and tibia are in contact. Patellar surface of the femur with the posterior surface of the patella patellofemoral joint Blood supply. A flatter condyle is more likely to result in patellar dislocation.
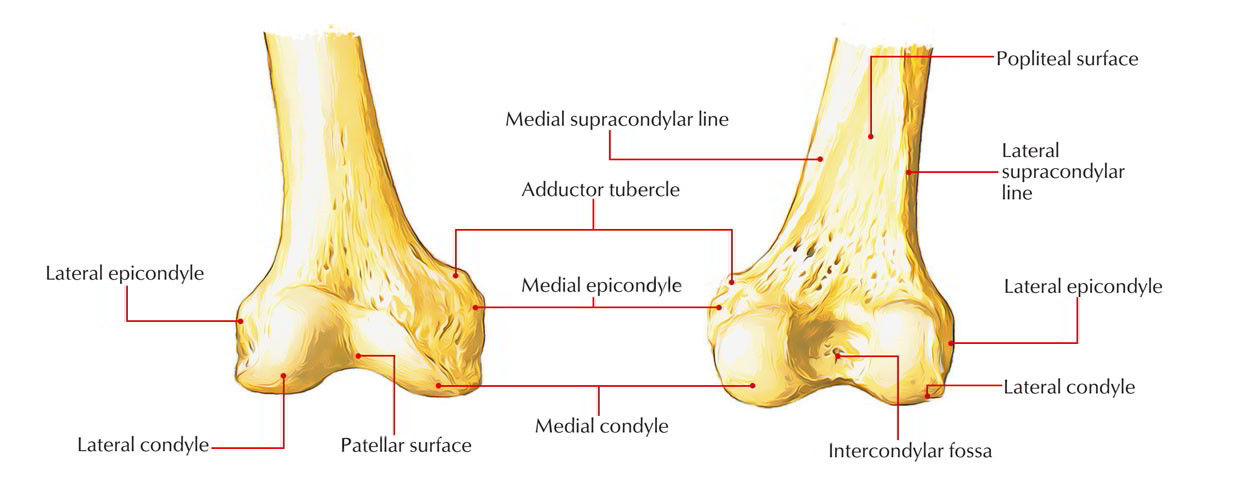
Posteriorly these condyles are separated by the deep intercondylar fossa. The more prominent lateral condyle helps prevent the natural lateral movement of the patella. The gluteal tuberosity is located on the proximal posterior femur very close to the proximal linea aspera.
Anteriorly on the distal femur is the smooth patellar surface which forms a joint with the patella or kneecap. The proximal tibia is widened by the medial and lateral condyles which aid in weight-bearing. The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur the other being the lateral condyle.
The medial and the lateral. The lateral epicondyle of the femur smaller and less prominent than the medial epicondyle gives attachment to the fibular collateral ligament of the knee-jointDirectly below it is a small depression from which a smooth well-marked groove curves obliquely upward and backward to the posterior extremity of the condyle. Ligament of head of femurThis short narrow ligamentous band transmits arteries to the head of the femur and helps attach the head to the acetabulum.
The shaft of the femur is a cylindrical shape and extends into two curved condyles at the distal end. One resembling a pair of knuckles. Lateral and medial condyles.
Anteriorly it is also attached to lateral menisci by transverse ligament and patella either directly or by patellomeniscal ligaments. The lateral cortex slopes at approximately 10 degrees and the medial cortex slopes approximately 25 degrees. However in the literature the focus has been on the sMCL which has been identified as a medial knee ligament connecting tibia with adjoining femur.
This structure articulates with the femoral condyles to form the key articulation of the knee joint. The synovial membrane of the joint capsule which is complete only in the horse further divides the joint into medial. Medial menisci are C shaped wedge fibrocartilagenous structure located between condyle of femur and tibia.
Outer iliac blade iliac crest sacrum coccyx Insertion. On the posterior surface of the condyle the linea aspera a ridge with two lips. The posterior and inferior surfaces articulate with the tibia and menisci of the knee while the anterior surface articulates with the patella.
Disorders of the femur. The MCL has a triangular shape. Lateral cortex of femur slopes 10 degree s medial cortex slopes 25 degrees in the axial plane posterior halves of both condyles are posterior to the posterior cortex of femoral shaft Muscles.
It is somewhat more in C shape as compared to lateral menisci as it is medial meniscus are clear of the plateau anteriorly and posteriorly. The distal aspect of the femur forms the proximal articulating surface for the knee which is composed of 2 large condyles. Medial and lateral condyles rounded areas at the end of the femur.
Lateral and medial condyles of the femur with the tibial plateaus of the tibia tibiofemoral joint. Neck of femur fractures slipped capital femoral epiphysis femoroacetabular. Iliotibial band of fasciae latae Action.
Located between the condyles is a region called the intercondylar eminence this projects upwards on either side as the medial. The unguallateral cartilages have a series of ligaments going to the mediallateral surfaces of the three phalanges and distal sesamoid. This article incorporates text in the public.
The medial condyle of the distal femur extends more distal than the. Connected along their length by. These two condyles are separated inferiorly by the intercondylar notch although they are connected anteriorly by a small shallow groove which is known as either the femoral sulcus or the patella groove or patella surface.
Iliac crest anterior iliac surface Insertion. Flexes abducts and medially rotates thigh.
Distal Femur Fracture Teachmesurgery
Orif Lag Screw For Lateral Medial Femoral Epicondyle Fracture
Femoral Condyle Articular Cartilage Injury Minneapolis St Paul Edina Eagan Mn
![]()
Lateral Femoral Condyle Anatomyzone


0 comments
Post a Comment